Optimization of Binary Superplasticized Concrete Using Taguchi Approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60787/ijtec.vol1no1.33Keywords:
Concrete, Superplastizer, Optimization, Compressive strength, TaguchiAbstract
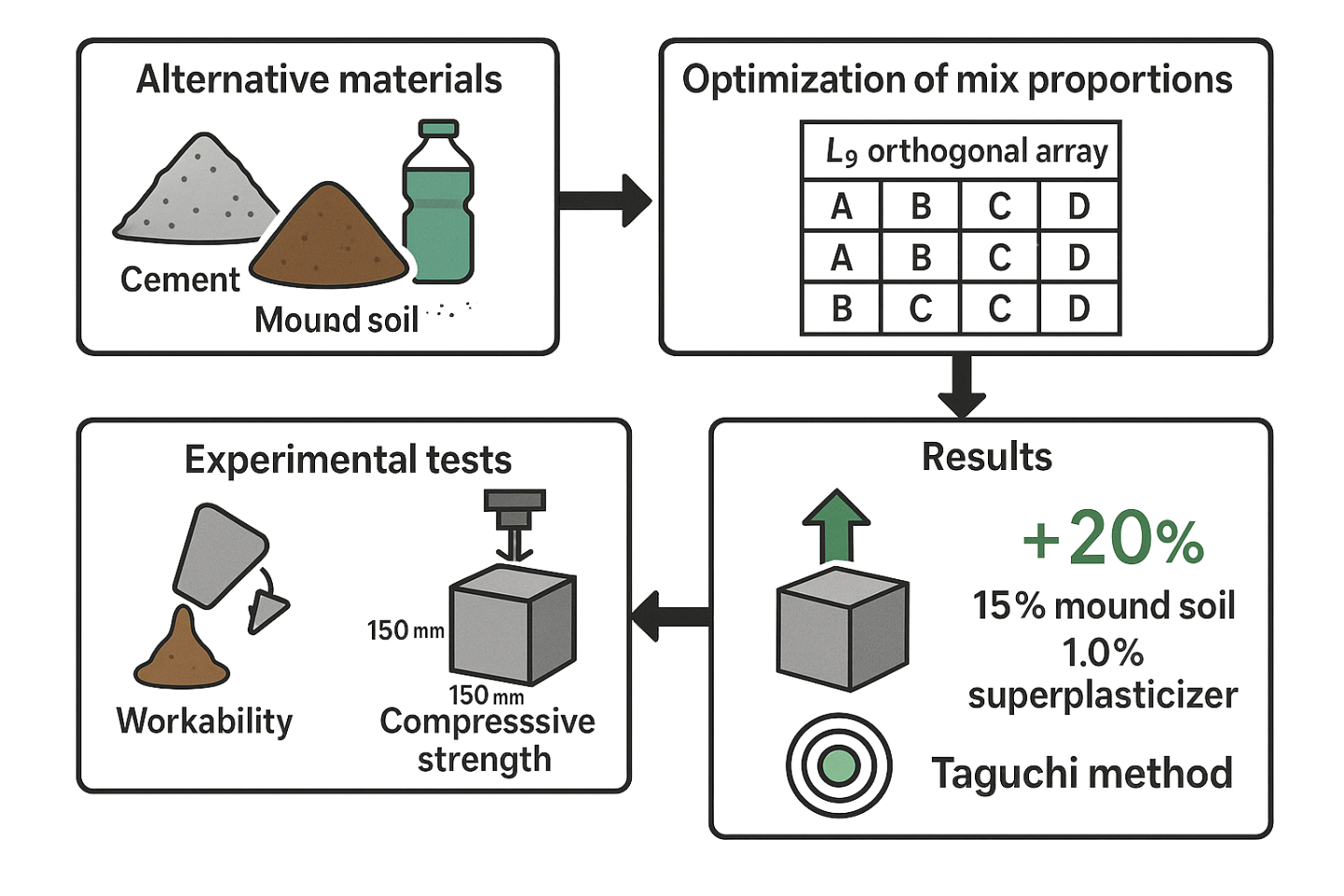
Several materials are being considered as replacements for cement and the other basic known ingredients of concrete, which would help to reduce cost and environmental hazards. This research involved investigating mix proportion parameters of binary superplasticized concrete comprising chemical superplasticizer and mound soil to develop an optimum design using the Taguchi Experimental design approach for high strength concrete. To achieve this objective, an L9 orthogonal array was employed, involving four key variables: water-to-cement ratio, cement quantity, mound soil proportion, and superplasticizer dosage. Each factor was assessed at three distinct levels. Concrete samples were molded into standard 150 mm cubes and evaluated in both fresh and hardened states. In the fresh condition, workability was analyzed, whereas the hardened samples were subjected to compressive strength testing at 7 and 28 days. The goal was to meet structural and functional standards for superplasticized concrete. Findings indicated that the optimal mix configuration—featuring 15% mound soil substitution and 1.0% chemical superplasticizer—yielded a compressive strength improvement of approximately 20% at 28 days. The result of a verification experiment conducted using the optimum mixture proportions compared favourably with the model predicted by Taguchi method which shows that Taguchi model is a suitable approach that can enhance the properties of binary superplasticized concrete.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 International Journal of Tropical Engineering and Computing

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.











